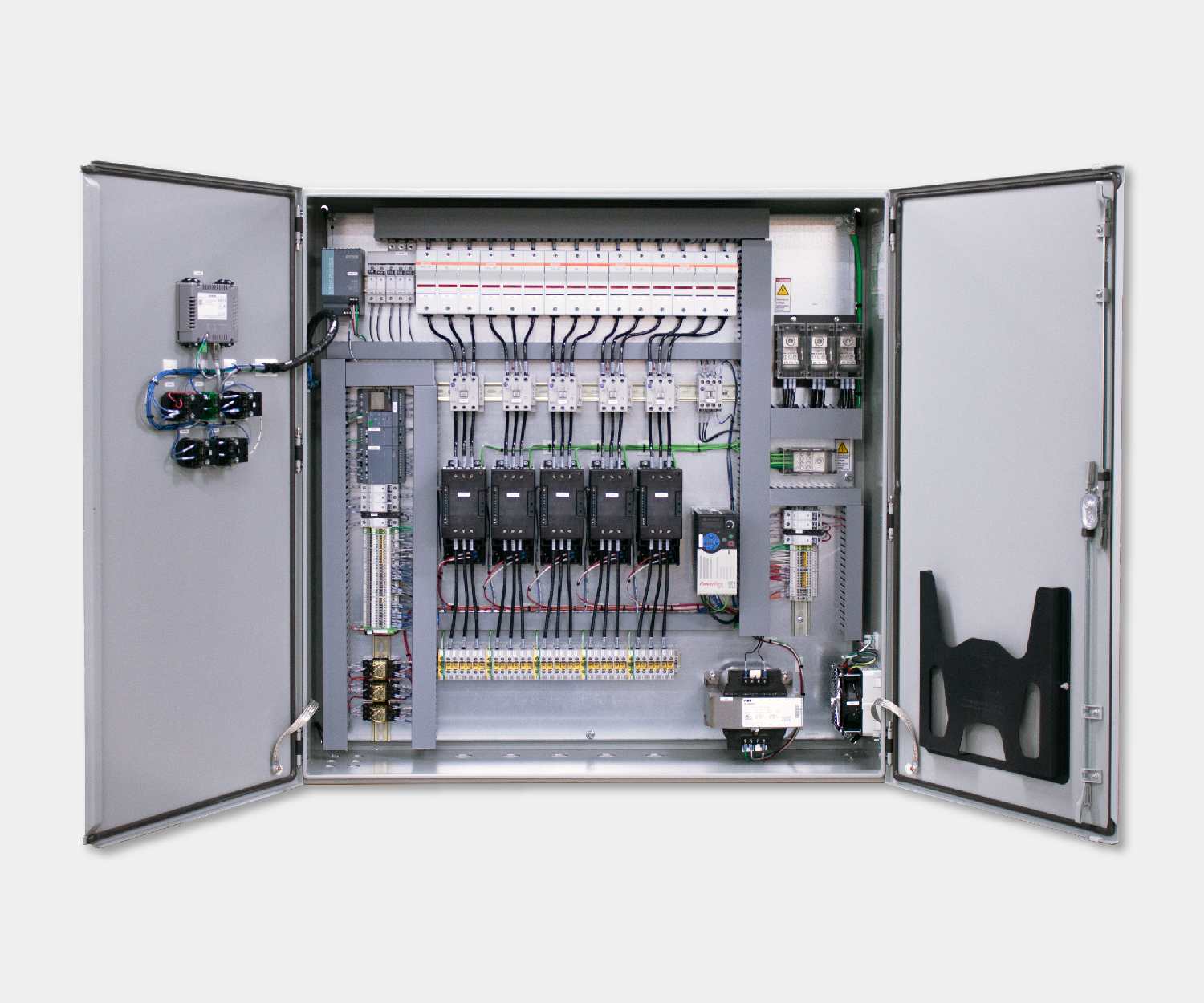
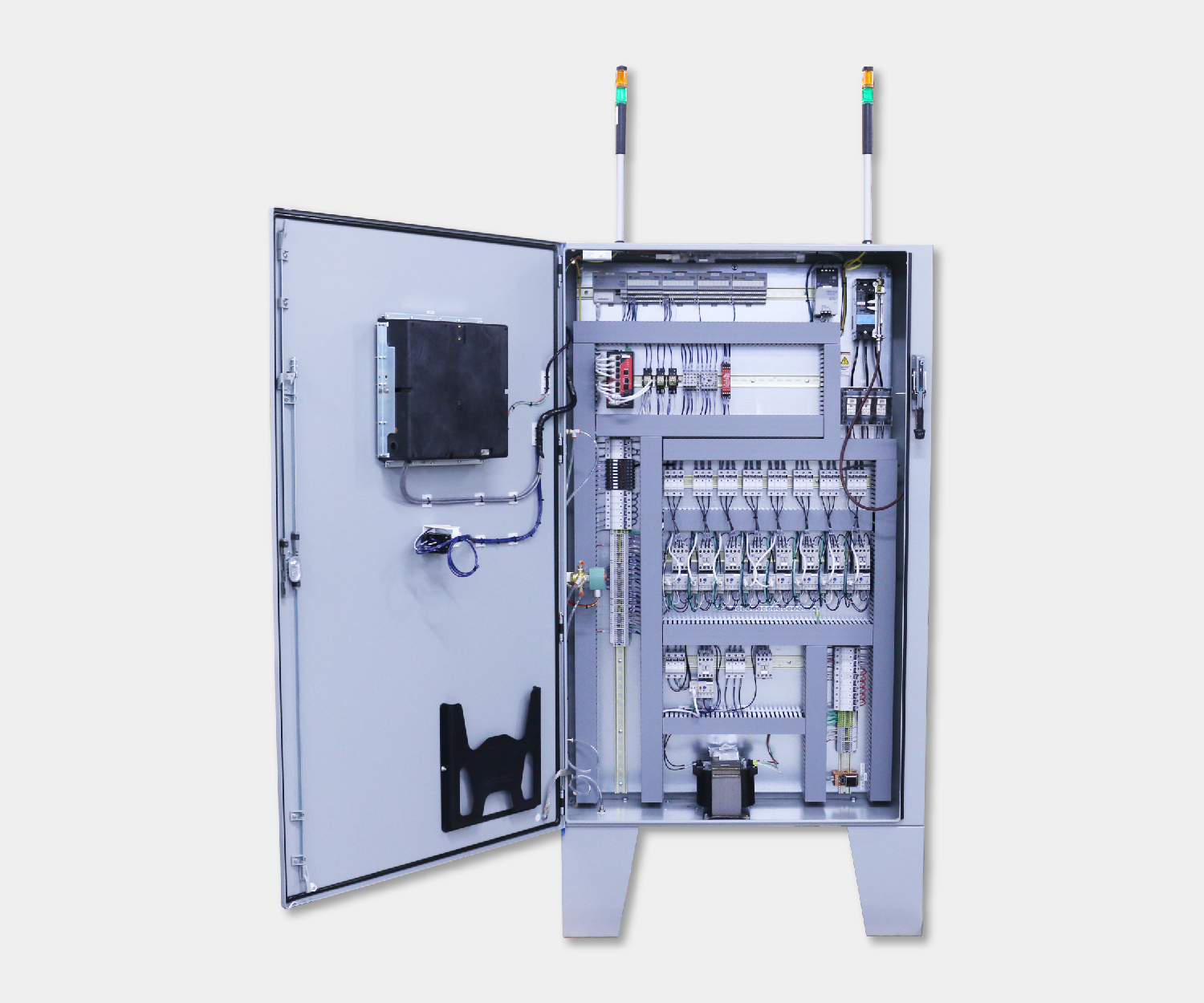
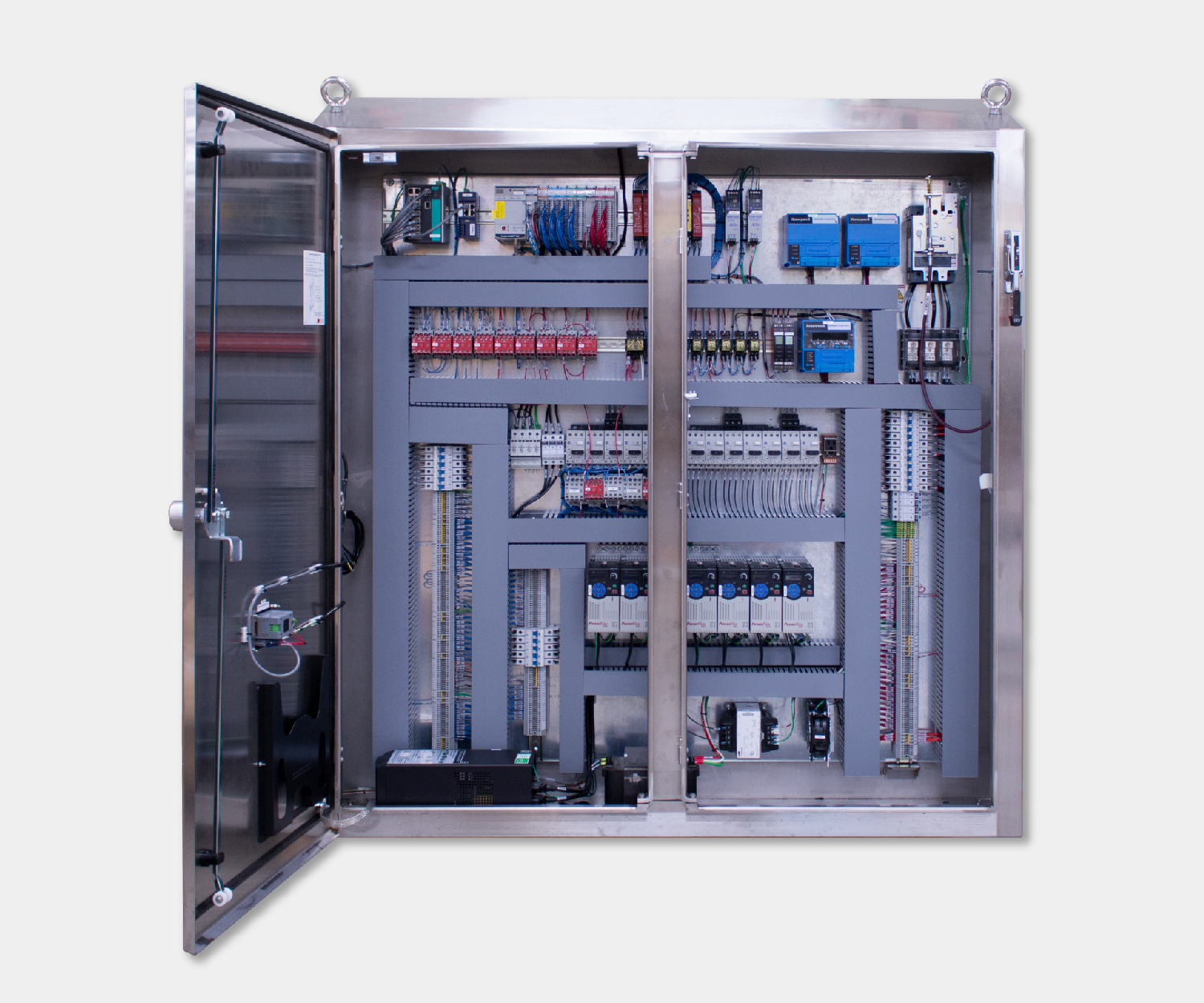
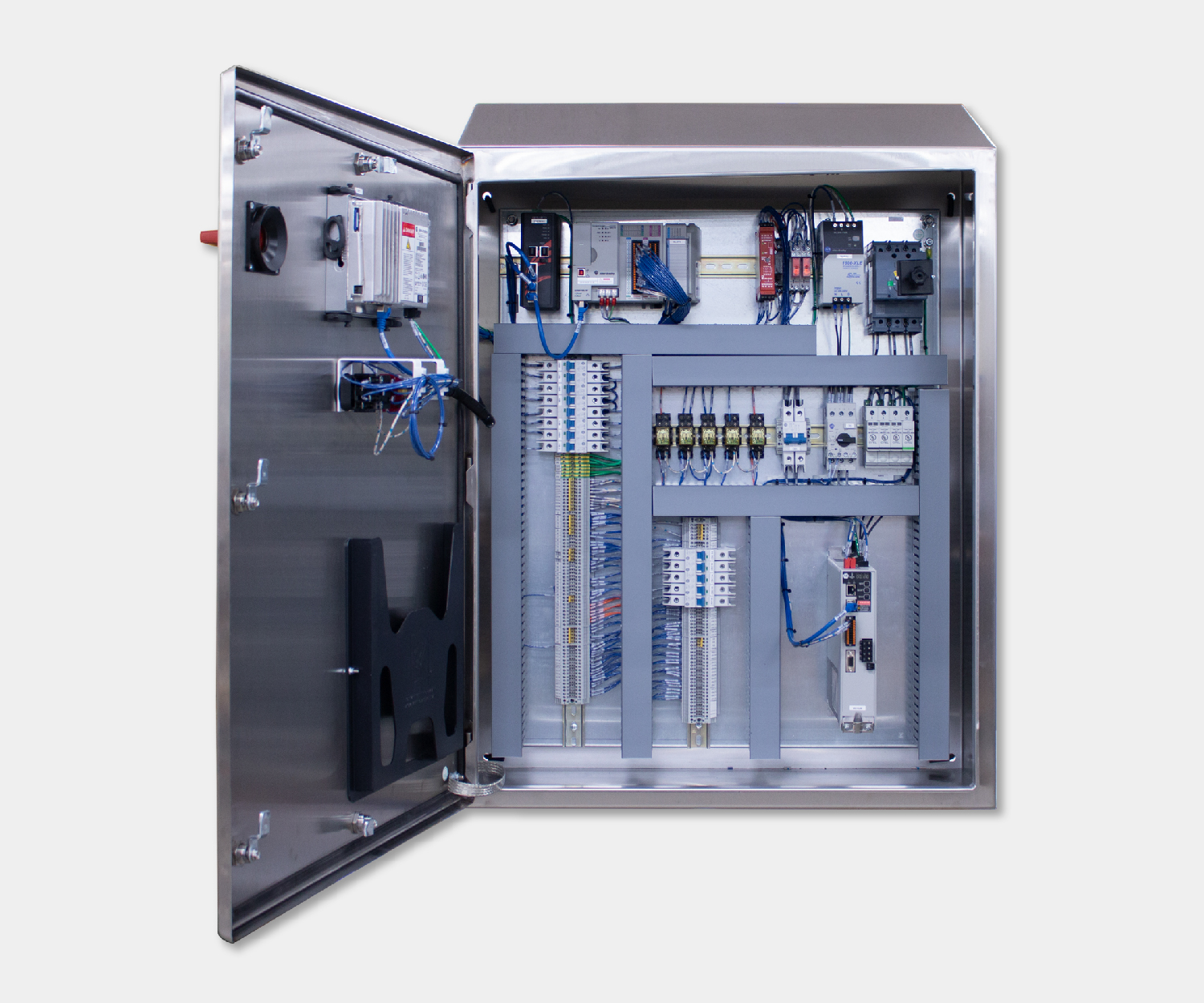
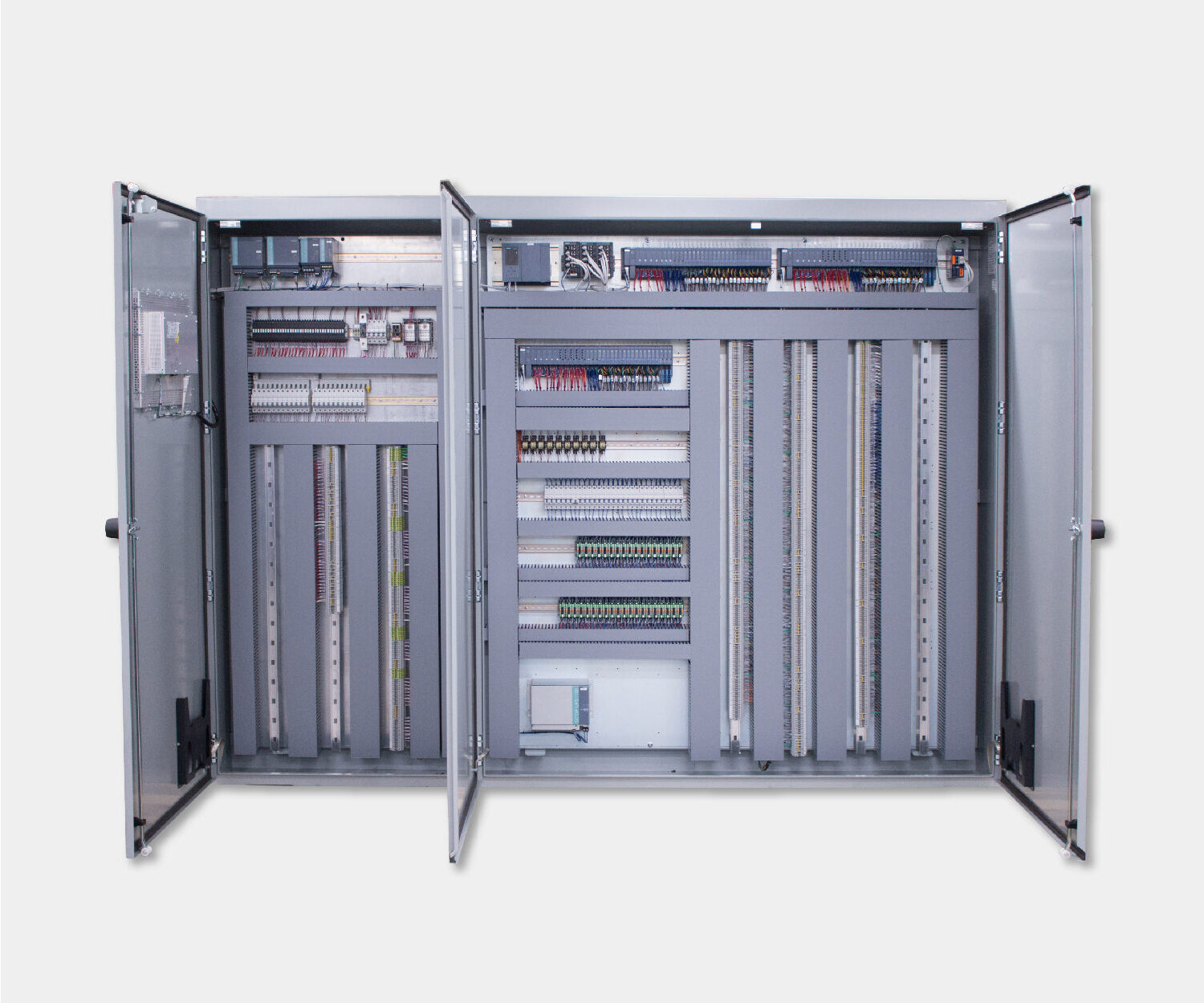
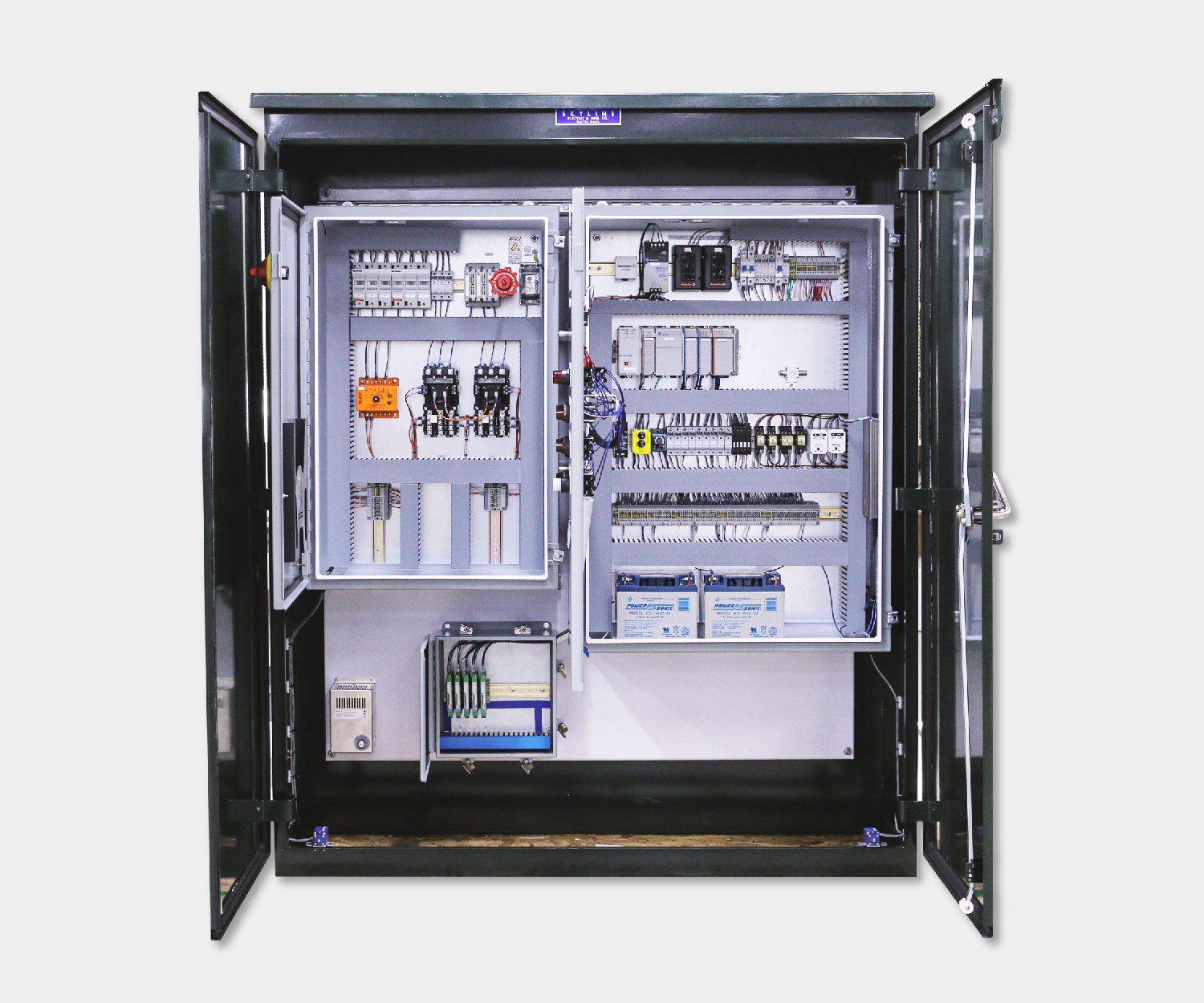
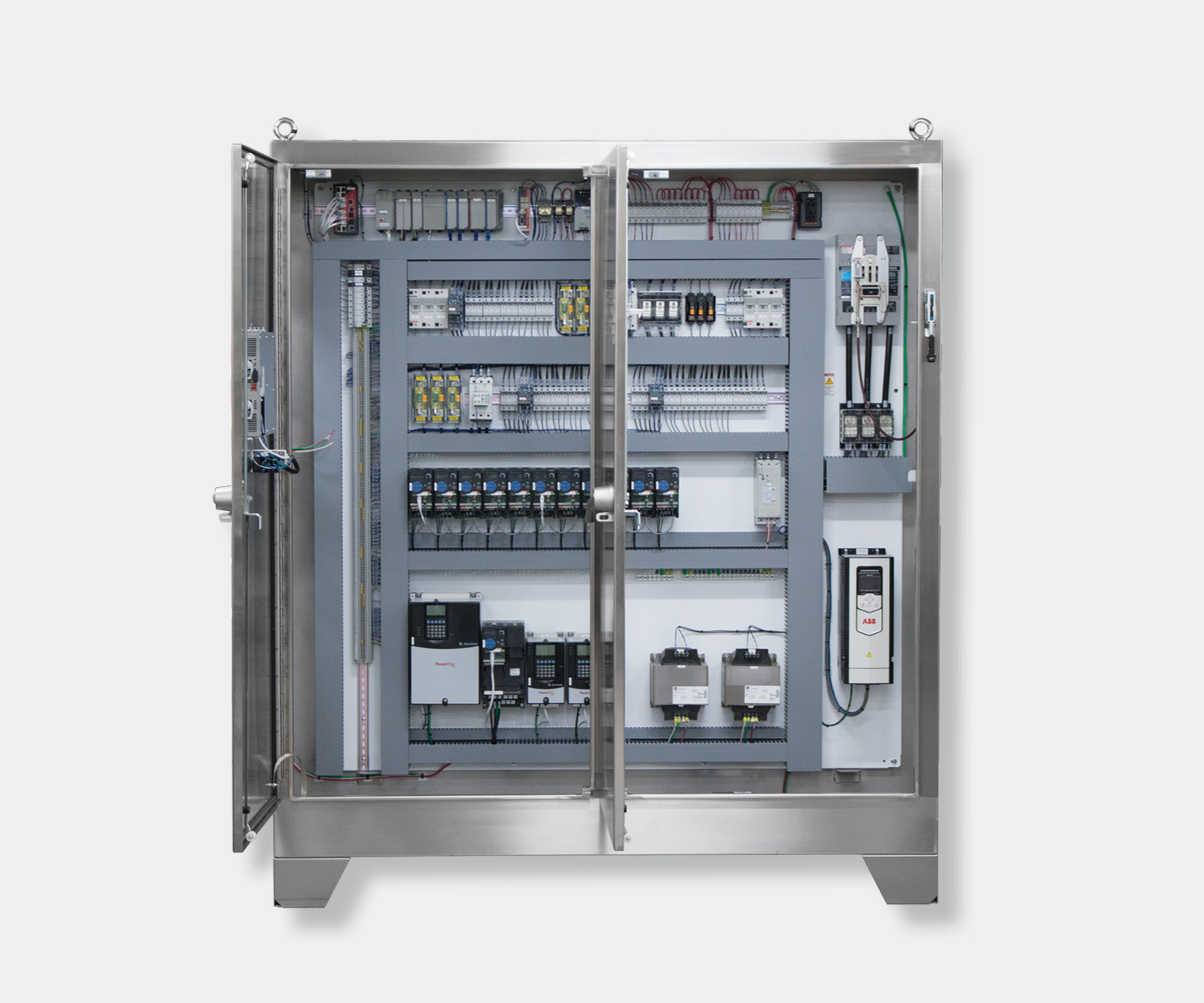
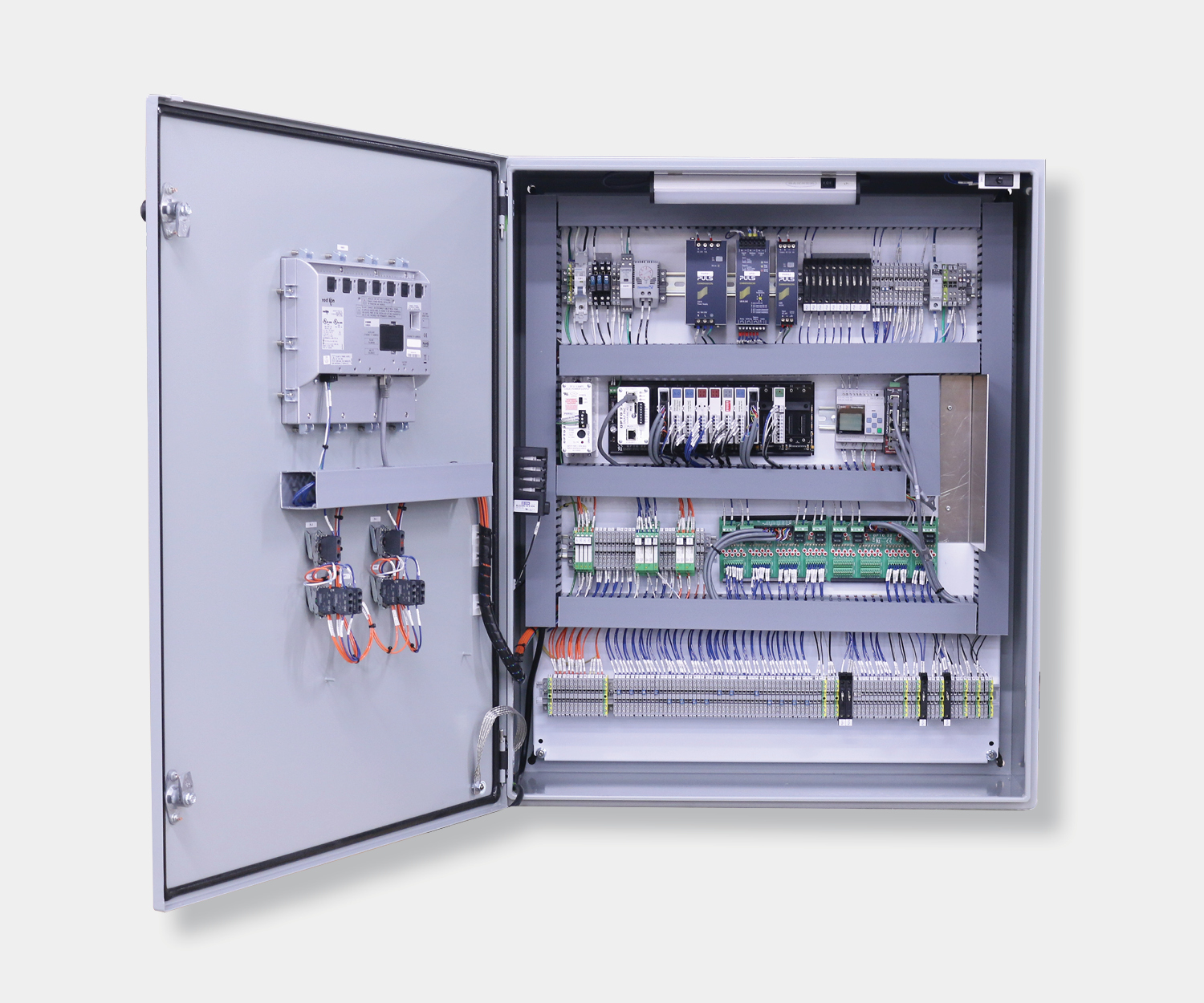
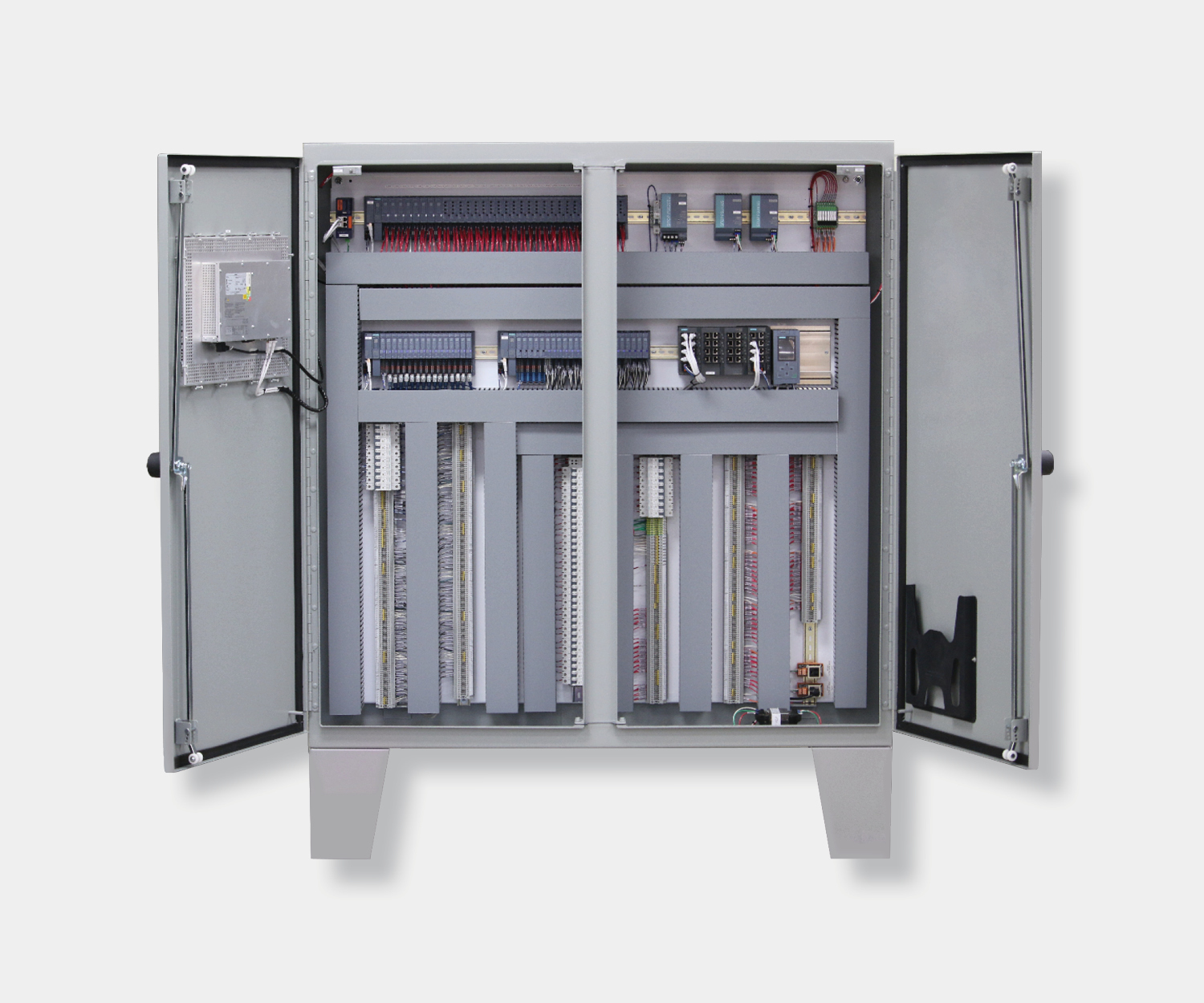
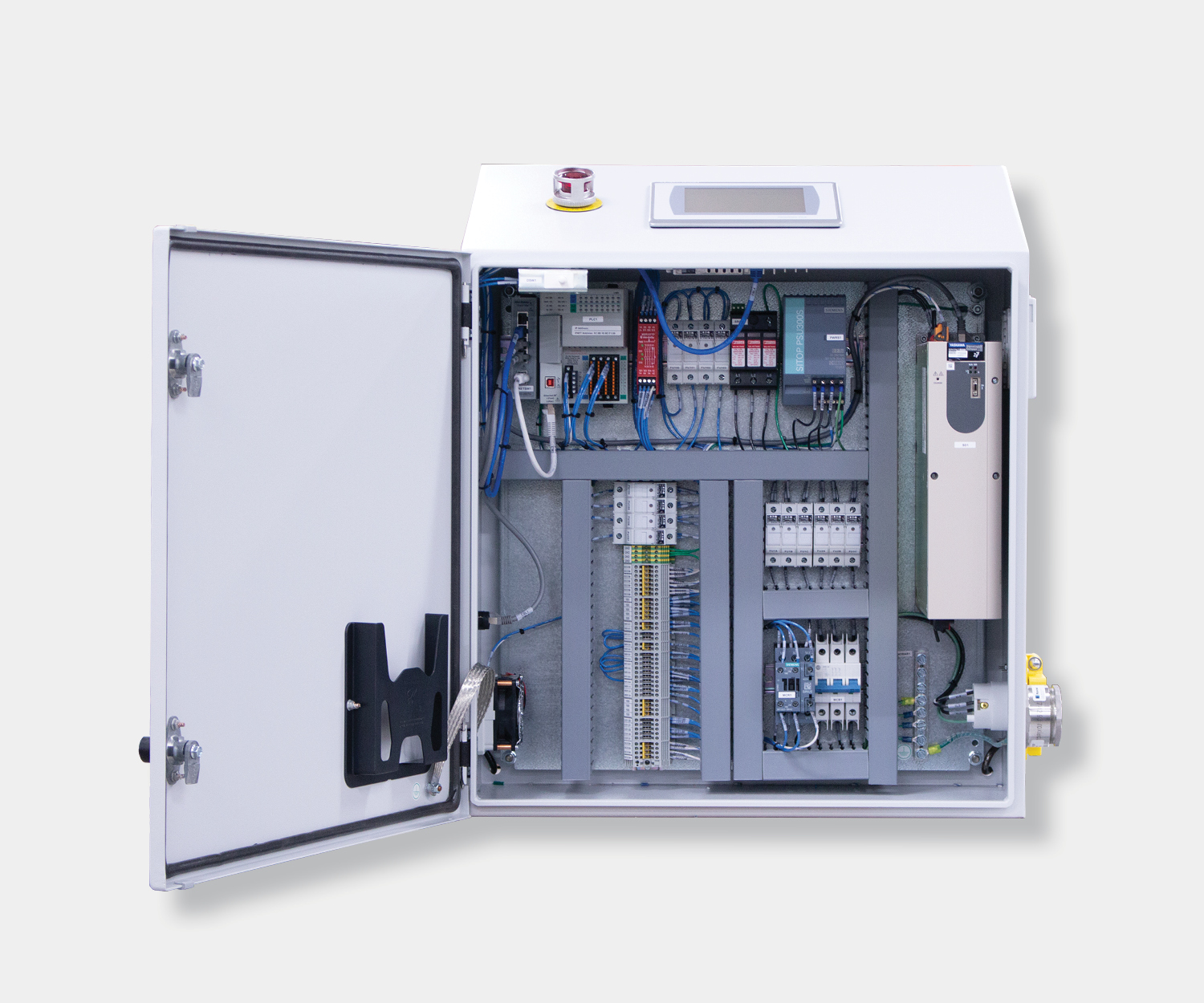
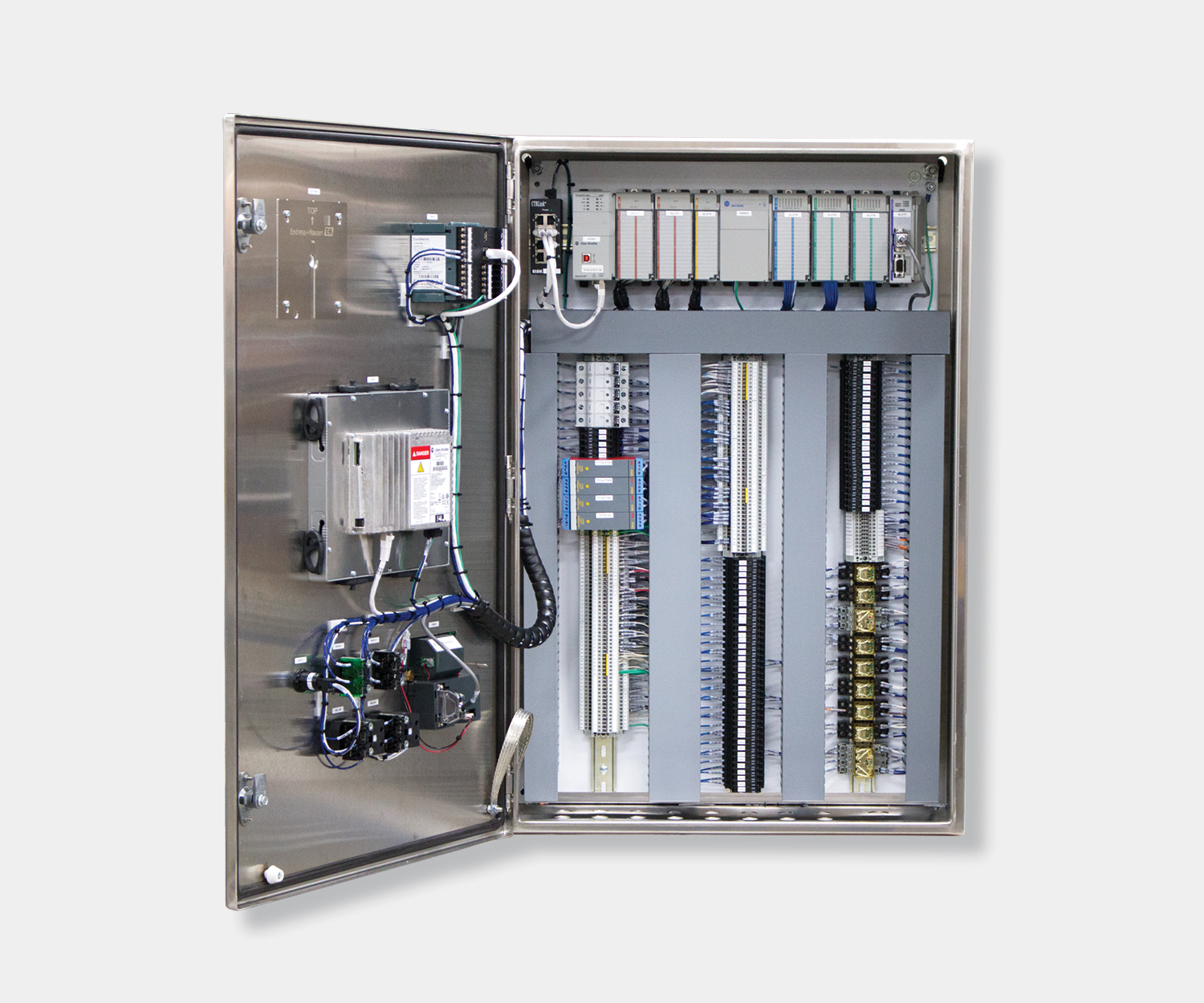
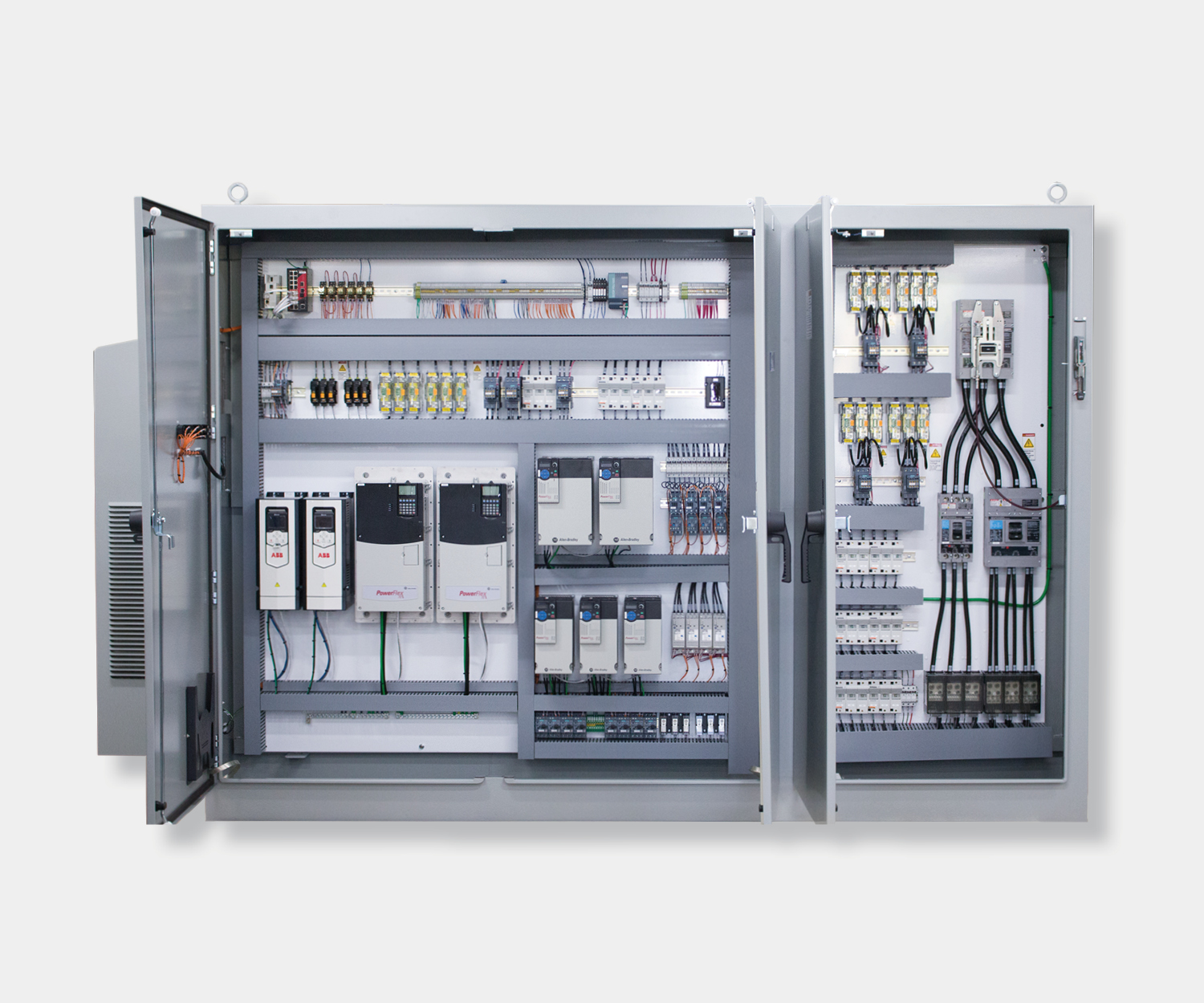
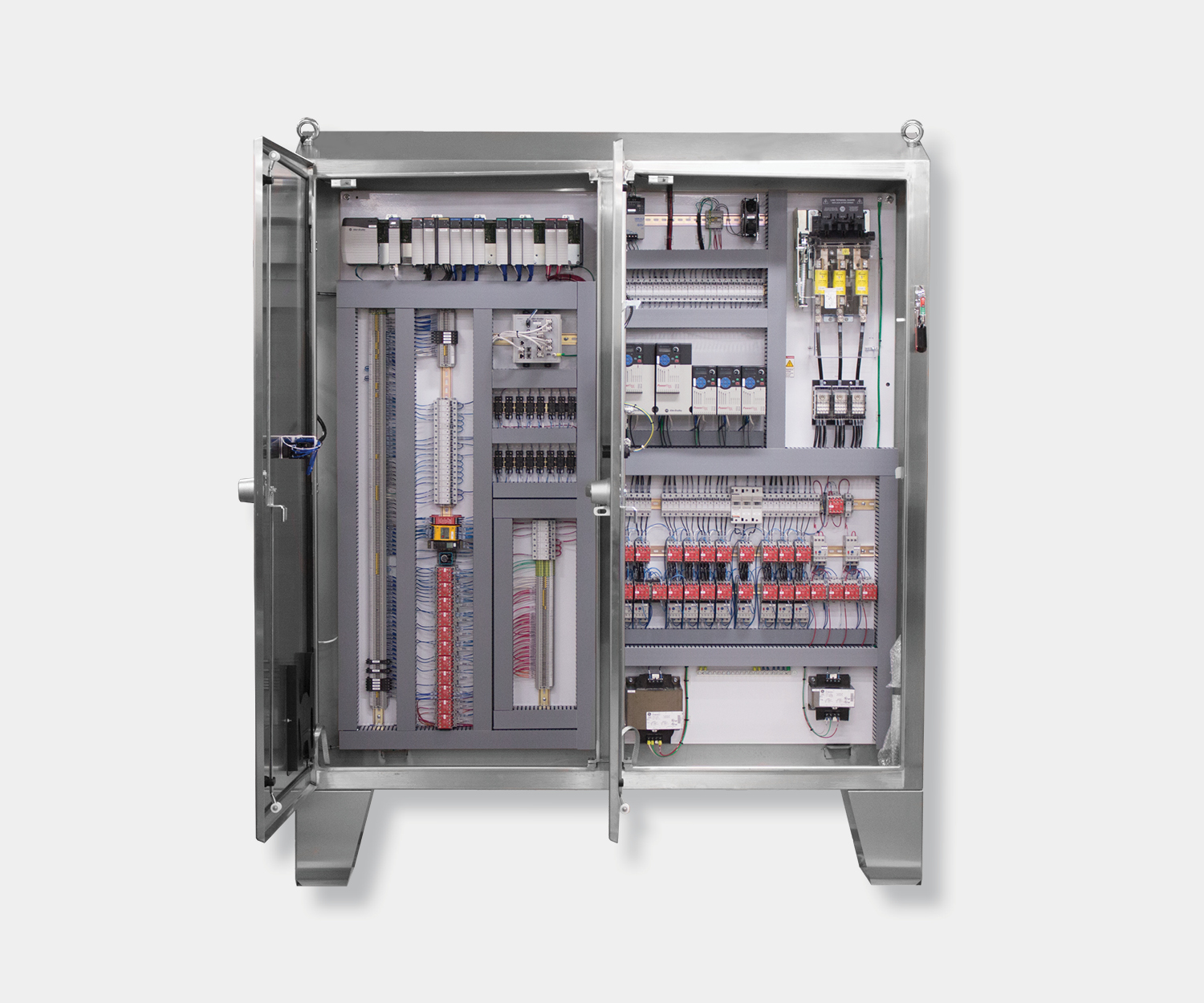
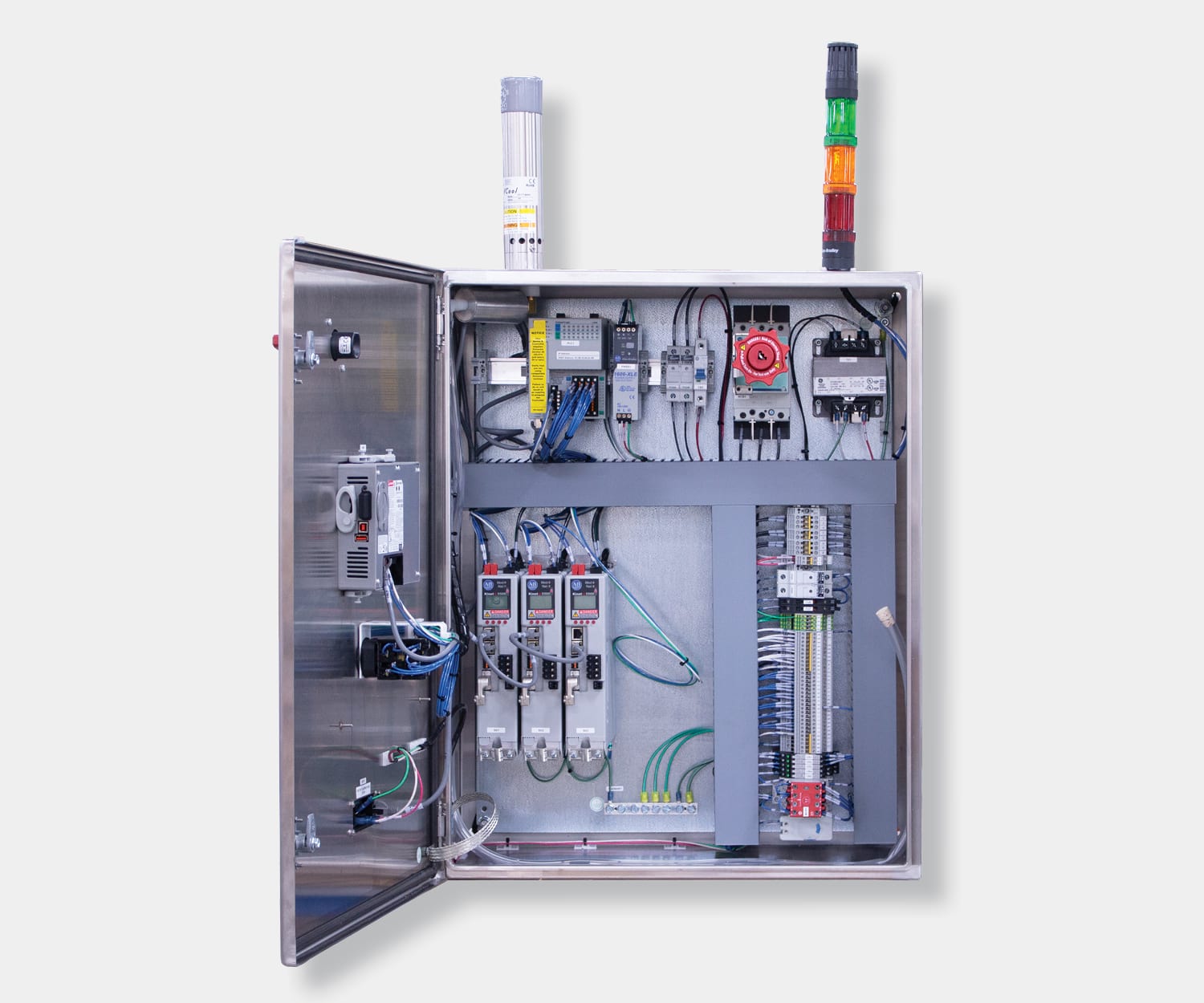
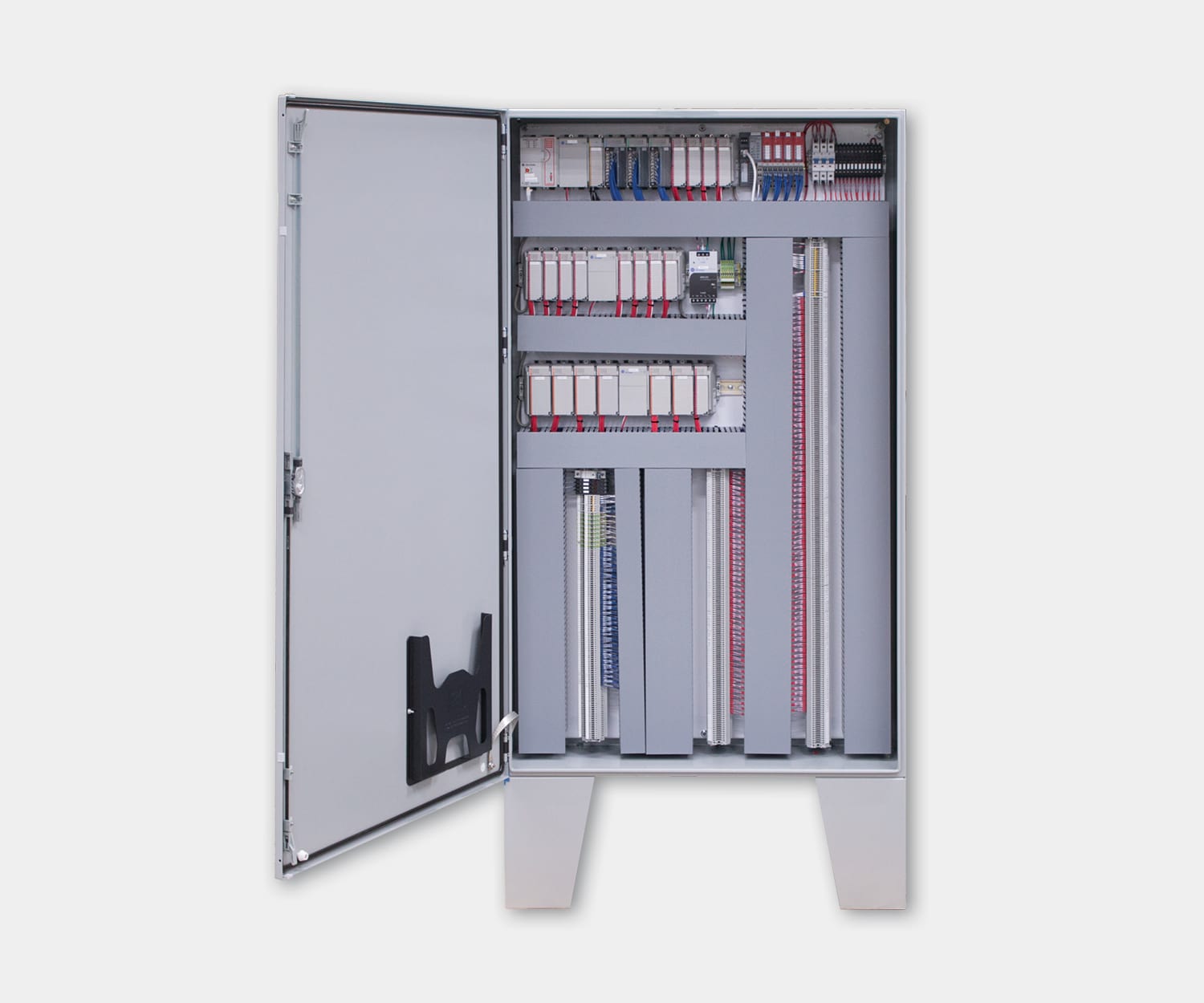
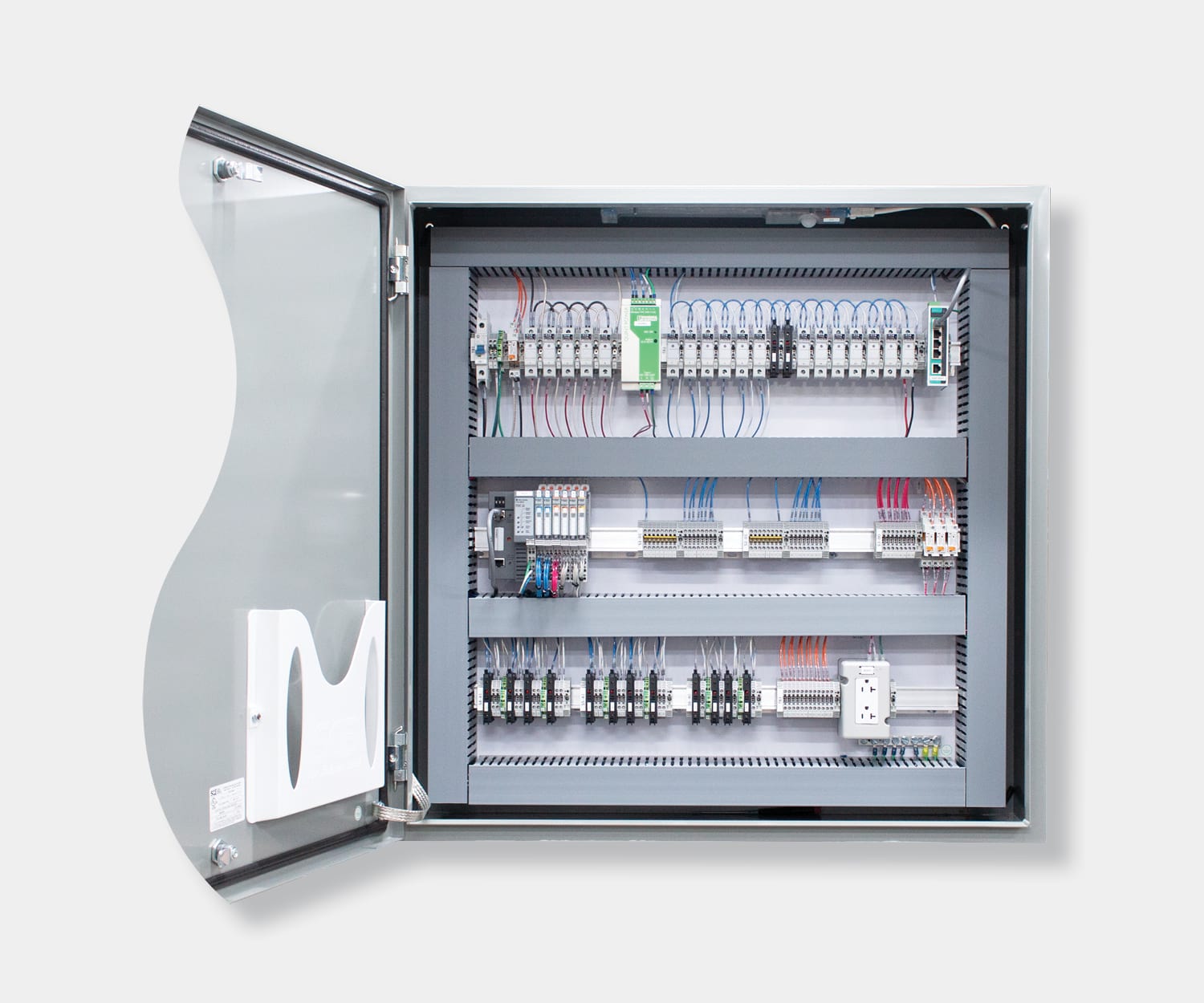
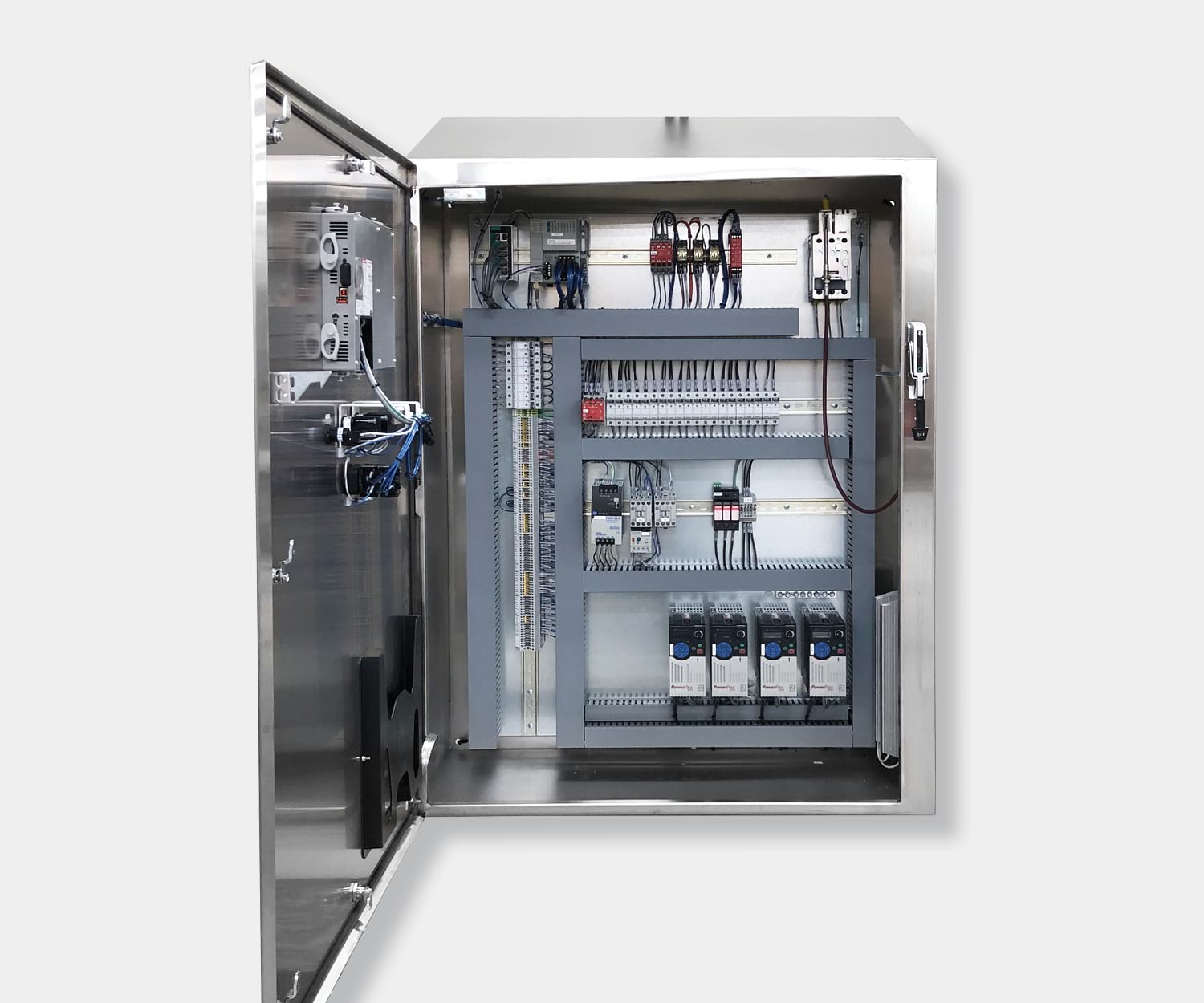
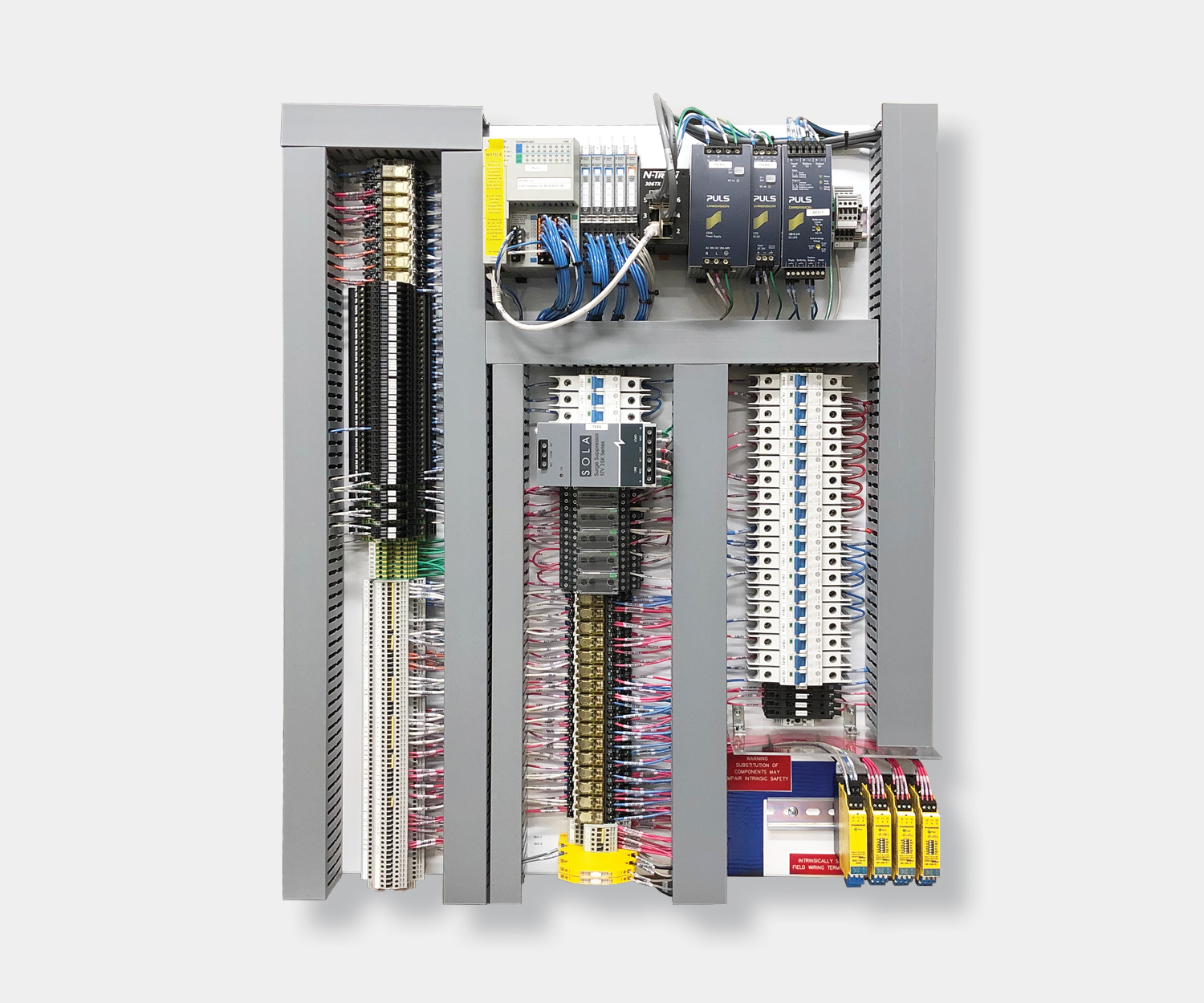
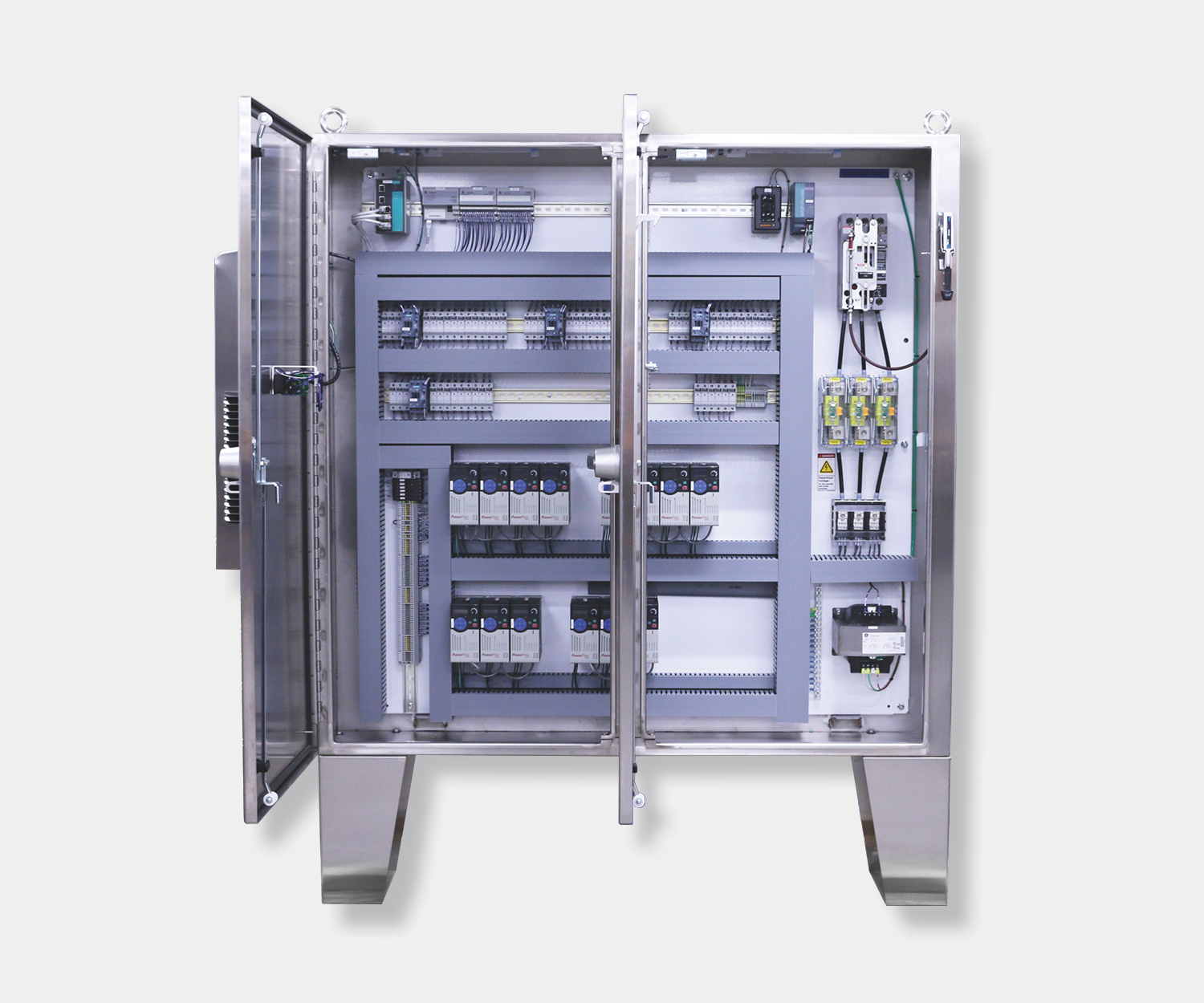
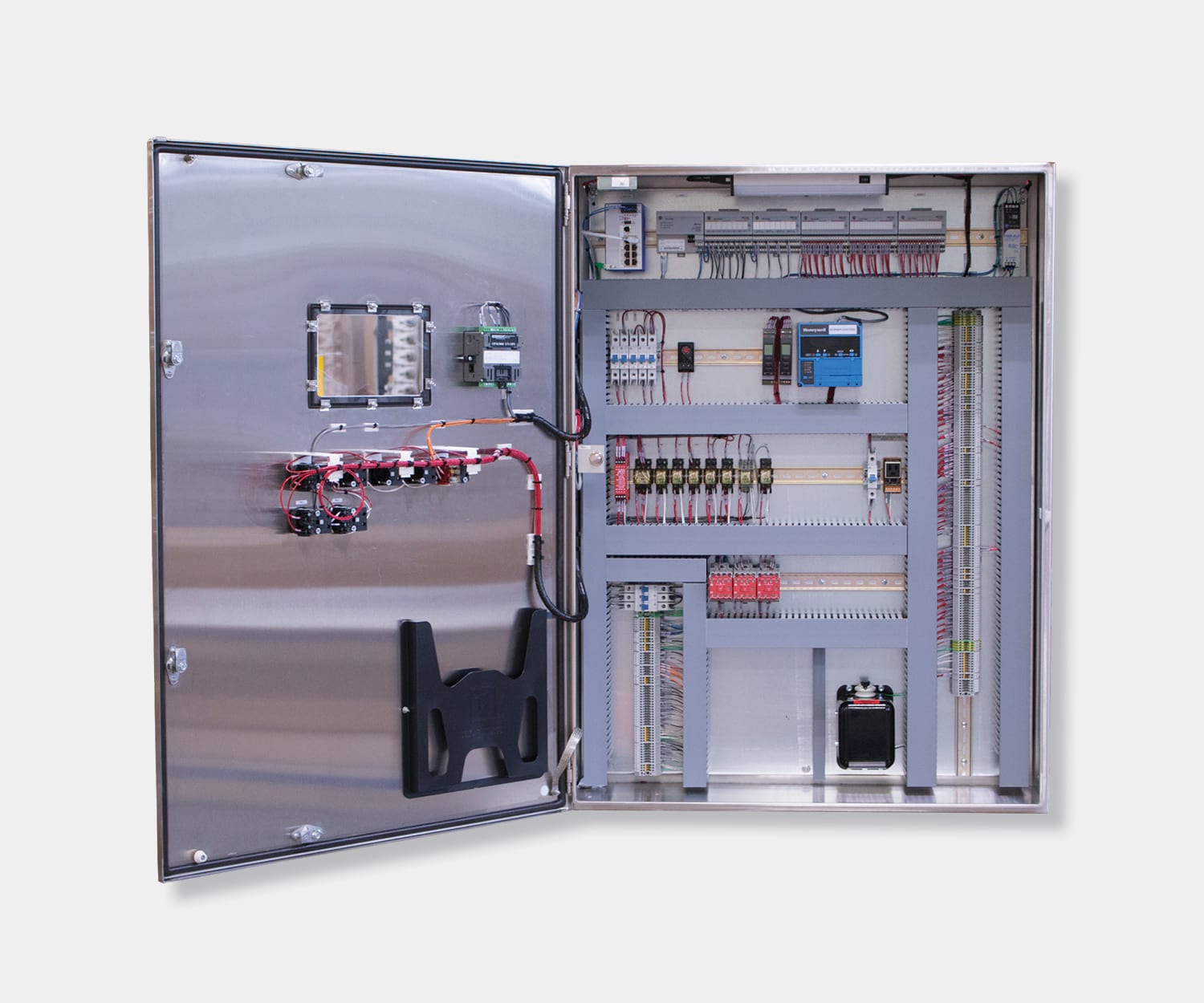
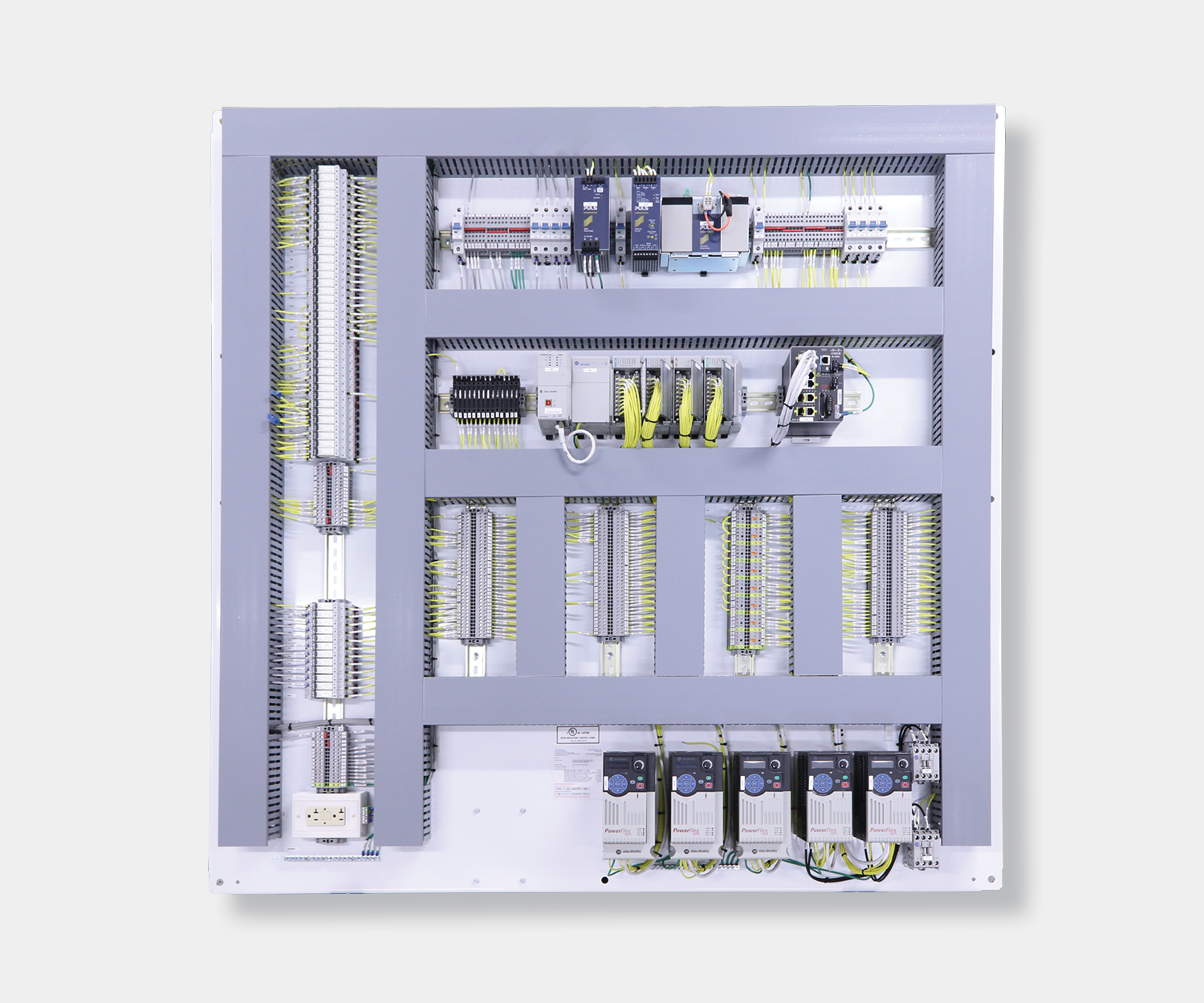
Electrical control panels are an integral part of any automated manufacturing process. At a basic level, control panels house various electronic devices that provide signals to direct the operation of equipment and machines. While control systems are a fundamental aspect of electrical engineering, many people aren’t aware of the key control panel components required to function safely and reliably.
Transformers
Transformers reduce or increase AC voltages between circuits. A common application for an industrial control panel transformer would be converting incoming 480V AC to 120V AC so the control panel’s other housed devices can use it.
Power Supply
A power supply converts alternating current (AC) voltage to direct current (DC) voltage. In a control panel, the power supply will typically be converting 480V AC or 120V AC to 24V DC.
Circuit Breakers
Circuit breakers protect an electrical circuit from becoming damaged by detecting when there is excess electrical current and opening or breaking the circuit to stop the flow.
Disconnect Switch
While a disconnect switch can come in many different styles and form factors, the overall purpose is to completely disconnect the control panel from its electrical supply. A common use for a disconnect switch is to shut off power to the control panel to complete repairs or maintenance, as well as for emergency stoppages.
Terminal Blocks
Terminal blocks are connection points that can join two or more wires together. It is possible to arrange terminal blocks together in a strip to direct power from one source to various devices in the control panel.
Relays
A relay is an electronically or magnetically operated switch that makes or breaks contact to turn on or off a device. Relays typically allow low currents to activate higher currents. The relay can achieve this activation by directing the lower current to flow through an input circuit and activating an electromagnet. The charged electromagnet then pulls the output circuit closed, allowing a higher current to flow through the output circuit.
Contactors
Similar to a relay, a contactor switches an electrical current on or off. The main difference between a contactor and a relay is that contactors are usually larger and used in applications with higher currents, where a relay is for lower currents. A common use case for contactors is for controlling electric motors, which often have high-current loads.
Overload Relay
An overload relay protects electric motors from overheating by preventing the motor from pulling more amps than the overload allows. This can occur when the motor’s circuit is being protected by a circuit breaker with a higher amp limit than the motor’s full-load rating. The overload relay protects the motor by opening the circuit when the current becomes 115% to 125% of the motor’s full-load rating.
Fuses
A fuse is a safety device that protects an electric circuit from becoming overloaded by a current that is too high. Once a fuse has operated, it becomes an open circuit and you must replace it.
Motor Drives
While there are numerous types of motor drives that each serve a specific purpose, the overall function is to operate a connected motor. Common motor drives used in control panels include VFDs, Servo Drives, and soft starters.
Motor Starters
A motor starter is a device that combines a contactor and an overload relay to control the electrical output from the motor during start-up, as well as provide overload protection while the motor is operating. A motor starter often has a modular assembly and includes a manual on-off switch.
Programmable Logic Controller (PLC)
A programmable logic controller or PLC is an industrial computer specifically designed for the control of manufacturing processes, such as moving equipment and machines on an assembly line. PLCs are programmed using a specific computer language and are designed to operate in factory conditions that may include high levels of noise and vibrations. To control equipment and processes, PLCs monitor the status of sensor inputs to control outputs, such as motors, HMI displays, valves, lights, and solenoids.
Ethernet Switch
An industrial Ethernet switch allows for communication between devices inside the control panel, such as PLCs, VFDs, and HMIs, as well as networked devices outside of the panel, such as other control panels, SCADA systems, or information systems.
About Process Solutions
Located near Seattle Washington, Process Solutions is the Northwest’s largest control systems integrator. With 30+ years in business and over 100 engineers and technicians on staff, Process Solutions has the experience and capacity to take on almost any automation project. Process Solutions provides a wide range of control system services, including electrical control panels, PLC and HMI programming, robot system integration, energy management and refrigeration systems, SCADA software, and machine monitoring software.